Howell-Jolly bodies
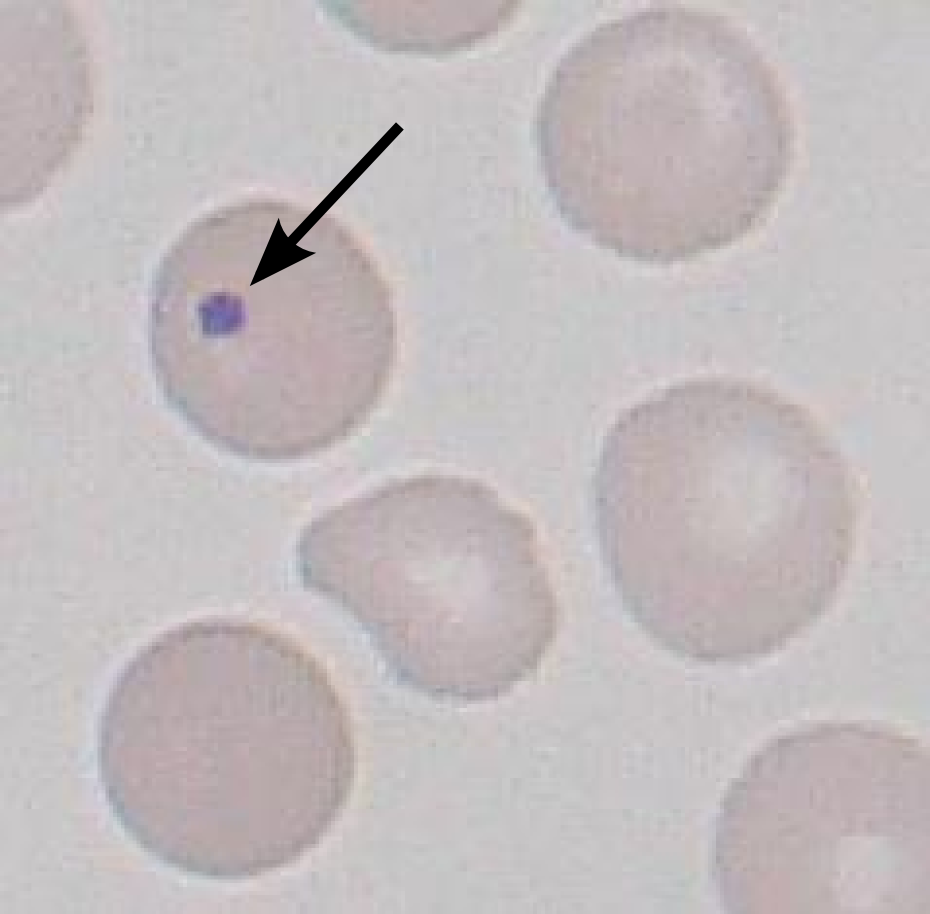
What is the diagnosis of the Image?
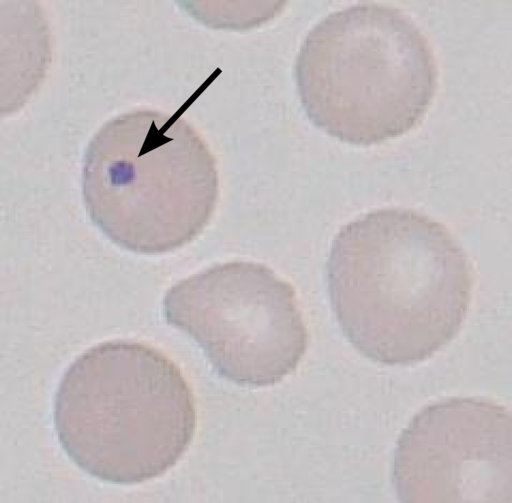
How the ‘Howell-Jolly bodies’ is produced?
In the bone marrow, late erythroblasts normally expel their nuclei; but, in some cases, a small portion of DNA remains which appears as Howell-Jolly bodies.
What is the clinical significance of presence of ‘Howell-Jolly bodies’ in peripheral smear?
Normally a healthy spleen removes red blood cells with ‘Howell-Jolly bodies’.
Presence of ‘Howell-Jolly bodies’ in peripheral smear suggests damaged or absent spleen,
Most common cause of ‘Howell-Jolly bodies?
‘Howell-Jolly bodies’ – Most commonly present in patients with absent or impaired function of the spleen
What are the causes of ‘Howell-Jolly bodies’?
Howell-Jolly bodies – pathognomonic for splenic dysfunction, but can be found in other disorders:
- post-splenectomy,
- sepsis,
- congenital disorders,
- sickle cell hemoglobinopathies,
- alcoholism,
- lupus and other autoimmune disorders,
- post-bone marrow transplantation.
Howell-Jolly bodies

Arrow show – Howell-Jolly bodies
Target cells (codocytes)

Target cells (codocytes)
Bullseyes appearance of Cells
Target cells (codocytes) appear as bullseyes, seen in
- liver disease,
- alpha/beta thalassemia,
- hemoglobin C disease
- asplenia
Spherocytes

Spherocytes
Spherocytes, noted by the lack of a pale center can been seen most commonly in
- hemolytic anemia
- hereditary spherocytosis)
Schistocytes & helmet cells

Schistocytes & helmet cells
Schistocytes (red arrow) and helmet cells (blue arrow) are common in –
Mechanism – shearing or mechanical destruction of the red cells. –
Diseases –
- disseminated intravascular coagulation
- thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
3, aortic stenosis.
